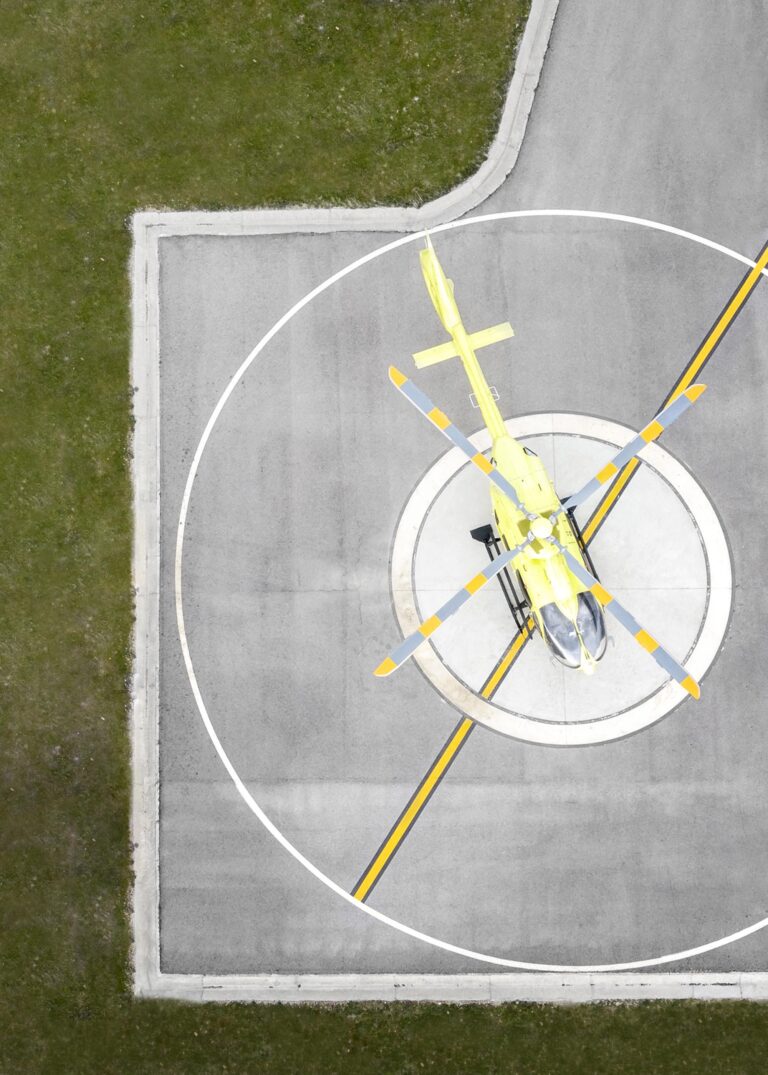
Helideck Inspection
Helideck Inspection
CAP 437, the Civil Aviation Publication by the UK Civil Aviation Authority, provides essential standards for the inspection and maintenance of offshore helidecks to ensure safety and compliance. Here is a detailed process for conducting helideck inspections according to CAP 437 standards:
1. Preparation and Pre-Inspection Checks
Before conducting a helideck inspection, it’s important to prepare by reviewing previous inspection reports, maintenance logs, and any relevant documentation. Inspectors should:
•Review maintenance history and previous inspection records to note any recurring issues.
•Ensure that all necessary inspection tools and equipment are available, including a camera, measurement devices, and PPE.
•Verify that all personnel involved are trained in CAP 437 standards and are familiar with inspection requirements.
•Coordinate with relevant onboard personnel and the helideck crew to minimize disruption to operations.
2. Surface and Structure Inspection
Inspecting the helideck’s surface and structure is crucial to ensure the deck can withstand operational demands and environmental conditions.
•Deck Surface Condition: Check for wear, corrosion, and any structural damage. The surface should be level, intact, and free of any protrusions or obstructions.
•Anti-Slip Coating: Confirm that the helideck surface has an effective anti-slip coating. Look for worn or damaged areas that could compromise safety.
•Drainage System: Inspect drains around the helideck to ensure they’re free from obstructions and functional. CAP 437 requires that no standing water accumulates on the helideck surface.
•Helideck Netting and Safety Markings: Inspect safety netting around the helideck, ensuring it is installed according to CAP 437 standards. Safety markings, such as the “H” landing marker, perimeter markings, and heliport identification should be clear, visible, and compliant with CAP 437 dimensions.
3. Fire-Fighting and Rescue Equipment
CAP 437 outlines specific requirements for fire-fighting and rescue equipment to mitigate potential fire risks on offshore helidecks.
•Fire Extinguishers: Confirm the type, quantity, and placement of fire extinguishers around the helideck. All extinguishers should be within their inspection dates and in working order.
•Deck Integrated Fire-Fighting System (DIFFS): Inspect the DIFFS, including spray nozzles, controls, and water/foam supply, ensuring they’re fully operational. Conduct a test activation, if permitted.
•Rescue and Firefighting Gear: Check the availability and condition of personal protective equipment (PPE) for fire response, including suits, gloves, helmets, and boots.
•Emergency Lighting: Ensure that emergency lighting is functional and meets the CAP 437 visibility requirements for night operations.
4. Visual Aids for Navigation
Helideck navigation aids are essential for safe landing and take-off operations, especially in low-visibility conditions.
•Lighting System: Inspect perimeter lighting, floodlights, and obstacle lights. Ensure lights are bright, clean, and in compliance with CAP 437 brightness and positioning standards.
•Windsock: Confirm the presence and condition of the windsock. It should be clearly visible, appropriately positioned, and free of damage.
•Helideck Identification and Markings: All signage and markings, including the heliport name, emergency exit signage, and helideck load limits, must be clearly visible and legible.
•Approach Path Obstacle-Free: Check for any obstructions in the approach or departure paths that could impact helicopter operations. CAP 437 mandates a clear “Obstacle-Free Sector” (OFS) for safe approach and take-off.
5. Safety Equipment and Operational Procedures
Helidecks must be equipped with specific safety systems and operational protocols.
•Friction Testing: Conduct a friction test on the helideck surface to ensure the anti-slip coating remains effective and meets the minimum required coefficient of friction.
•Helicopter Tie-Down Points: Inspect tie-down points for secure anchorage and absence of corrosion or structural weakness. CAP 437 requires tie-downs to support a helicopter during strong winds.
•Weather Monitoring Equipment: Ensure that all meteorological equipment, such as wind speed indicators, is functioning correctly to provide accurate data to pilots.
•Fueling System Inspection: If the helideck is equipped with fueling systems, check the hoses, filters, grounding systems, and storage tanks to ensure they meet CAP 437 safety standards.
6. Documentation and Record-Keeping
Record-keeping is essential for compliance, maintenance, and inspection tracking. The following should be documented:
•Inspection Checklists and Findings: Complete a checklist to document findings for each component. Record any issues identified, with specific details on the location and nature of defects.
•Maintenance and Repairs Log: Note any immediate repairs made or scheduled maintenance needs.
•Inspection Photographs: Take photographs of critical areas, particularly where damage, wear, or non-compliance is identified.
•Action Items and Recommendations: Outline any necessary corrective actions, assigning responsibilities and deadlines. Follow up on unresolved items from previous inspections.
7. Final Review and Reporting
Upon completion of the inspection, conduct a review with relevant personnel to discuss findings, recommended corrective actions, and timelines. Submit a detailed inspection report that includes:
•Summary of Inspection Findings: Highlight key findings, with an emphasis on any non-compliance with CAP 437.
•Safety Recommendations: Provide specific safety recommendations based on identified risks.
•Follow-Up Plan: Establish a follow-up schedule for corrective actions, with a designated point of contact for each item.
By following these steps, helideck operators can ensure that offshore helidecks comply with CAP 437, maintaining a high level of safety for helicopter operations.